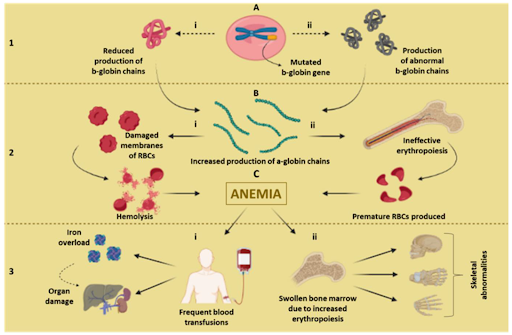
Thalassemia is a genetic blood disorder that affects the body’s ability to produce healthy hemoglobin. Hemoglobin is essential for carrying oxygen throughout the body, and when it is low, a person may feel tired, weak, or short of breath. Thalassemia is a lifelong condition, but with the right treatment and medical care, patients can live healthier and more active lives.
This article explains thalassemia treatment in simple, easy-to-understand language to help patients and families make informed decisions.
Understanding Thalassemia
Thalassemia is inherited from parents and is usually diagnosed in childhood. There are two main types:
- Thalassemia minor, which often causes mild or no symptoms
- Thalassemia major, a more severe form that requires regular medical treatment
The type and severity of thalassemia determine the treatment plan.
Goals of Thalassemia Treatment
The main goals of treatment are:
- Maintaining healthy hemoglobin levels
- Preventing complications such as organ damage
- Supporting normal growth and development
- Improving overall quality of life
Treatment is customized for each patient based on age, symptoms, and disease severity.
Blood Transfusions
Regular blood transfusions are the most common treatment for moderate to severe thalassemia. Transfusions help maintain healthy hemoglobin levels and reduce symptoms like fatigue and weakness.
Patients may need transfusions every few weeks, depending on their condition. While transfusions are effective, they can lead to iron buildup in the body over time, which requires additional treatment.
Iron Chelation Therapy
Frequent blood transfusions can cause excess iron to collect in organs such as the liver, heart, and endocrine glands. Iron chelation therapy removes this extra iron and prevents long-term damage.
Chelation medicines are taken orally or through injections and are an essential part of long-term thalassemia care.
Supportive Care and Medications
In addition to transfusions and chelation, patients may need:
- Folic acid supplements to support red blood cell production
- Hormone therapy if growth or puberty is delayed
- Regular monitoring of heart, liver, and endocrine function
Good nutrition and routine medical follow-ups play an important role in overall health.
Understanding Treatment Planning and Costs
Long-term treatment requires careful planning, including medical follow-ups, medication schedules, and hospital visits. Many families also seek information about the Thalassemia Treatment Cost in India as part of their decision-making, since expenses can vary based on transfusion frequency, chelation therapy, hospital choice, and advanced treatment options.
Bone Marrow Transplant: A Potential Cure
Bone marrow or stem cell transplant is currently the only known cure for thalassemia. It involves replacing diseased bone marrow with healthy stem cells from a matched donor.
This option is usually considered for:
- Children or young adults with severe thalassemia
- Patients with a well-matched sibling donor
- Individuals without major organ damage
While transplantation carries risks, it can offer a permanent solution for selected patients.
Emerging Treatments and Research
Medical research continues to improve thalassemia care. Newer treatment approaches include:
- Gene therapy, which aims to correct the genetic defect
- Improved chelation drugs with fewer side effects
- Better transfusion techniques to reduce complications
These advances are increasing life expectancy and improving quality of life for patients.
Living Well with Thalassemia
With proper treatment, many people with thalassemia lead productive lives. Important lifestyle tips include:
- Following the treatment plan consistently
- Eating a balanced diet
- Avoiding iron-rich foods unless advised by a doctor
- Staying physically active within safe limits
Emotional support from family, healthcare providers, and support groups is equally important.
Final Thoughts
Thalassemia is a lifelong condition, but modern treatments have made it highly manageable. From regular blood transfusions to advanced curative options, treatment plans are designed to meet each patient’s needs. Early diagnosis, proper medical care, and ongoing support can help individuals with thalassemia live longer, healthier, and more fulfilling lives.